The halving
As part of the Bitcoin protocol, the month of April 2024 will see an event called “halving” occur for the fourth time in the history of this cryptocurrency. The code provides that the reward paid to minors1 of bitcoins will increase from 6.25 bitcoins to approximately 3.13 bitcoins when the blockchain reaches 840,000 blocks. Therefore, the Bitcoin protocol provides for a “halving cycle” every 210,000 blocks, or approximately every four years. We've seen these events before: rewards started at 50, then went down to 25, then 12.5, and finally reached 6.25. The process will repeat until around 2040, at which point the reward per mined block will approach zero and all of the planned 21 million Bitcoins will be in circulation. Currently, approximately 19.7 million Bitcoins have been issued out of the 21 million limit.
Chart 1, which we have already looked at, shows that if we normalize the Bitcoin price on halving day to 1.0, we see further price appreciation in each of the three scenarios over the next 2.5 years or so. During each historical halving, which marks a stage in the Bitcoin cycle, we see that prices reach higher and higher highs, and also higher and higher lows.
Let's analyze Bitcoin from a supply and demand perspective. If demand exceeds supply, this should put upward pressure on the price. Halving involves a reduction in the number of new Bitcoins issued worldwide. Therefore, if demand remains unchanged, the balance between supply and demand immediately tilts toward demand exceeding supply.
Illustration 1: Evolution of the price of Bitcoin after the three previous halving cycles
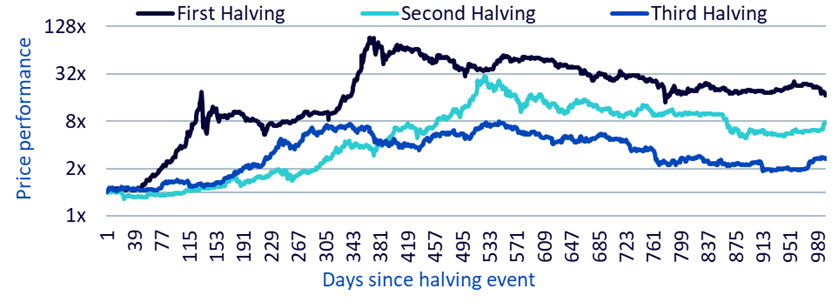
Source: Glassode, WisdomTree, December 2023. Reindexed to 1 from the halving date. Historical performance is no guarantee of future performance, and any investment may lose value.
Spot Bitcoin ETF: A New Source of Demand
One of Bitcoin's most valued attributes is the certainty of supply, written into the protocol's code since its inception. We know that in 2040, 21 million Bitcoins will be in circulation2 and we know that nothing can change that. In accordance with the halving protocol, we know that the creation of new units of Bitcoin is halved approximately every four years.
This approach is in direct contrast to fiat currency systems, in which governments can decide to print more units of currency without restrictions. Throughout history, we have seen many cases of fiat currencies losing their value and dominant currency status due to excessive use of “printing money”. We saw the US dollar lose value over time after the link to gold was severed in 1971, allowing the US government to print more money without it being backed by the precious metal.
It was speculated that if the Securities and Exchange Commission in the United States approved spot Bitcoin ETFs, new sources of demand for holding Bitcoin would emerge. In the same way that in 2004 a new option opened up for investors who did not wish to go through the hassle of acquiring and storing physical gold bars, in 2024 investors were allowed to gain exposure to spot bitcoin through the usual brokerage platforms where they trade ETFs backed by other types of assets.
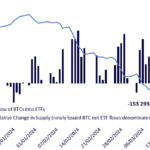
Today, a little over two months after their launch, we can analyze the evolution of Bitcoin supply and demand, and determine whether these ETFs have had a notable influence.
The illustration below allows us to formulate the following statements:
- Purchases exceeded sales: Before the launch of ETFs, among the assumptions made was the accessibility of exposure to a wider range of investors, notably those who could not set up their own crypto portfolios. The daily net flow of BTC into ETFs is decidedly positive, indicating a massive movement of BTC into these funds. It should be noted that many investors operate in companies whose internal supervisory bodies have not yet approved the use of these products.
- ETF purchases outpaced Bitcoin issuance: Bitcoin ETF purchases outpaced the creation of new Bitcoins by approximately 130,000 units during this period. Transparency reigns in this universe: we can track ETF purchases, portfolios and the length of time since individual units moved.
Illustration 2: ETF demand versus Bitcoin issuance
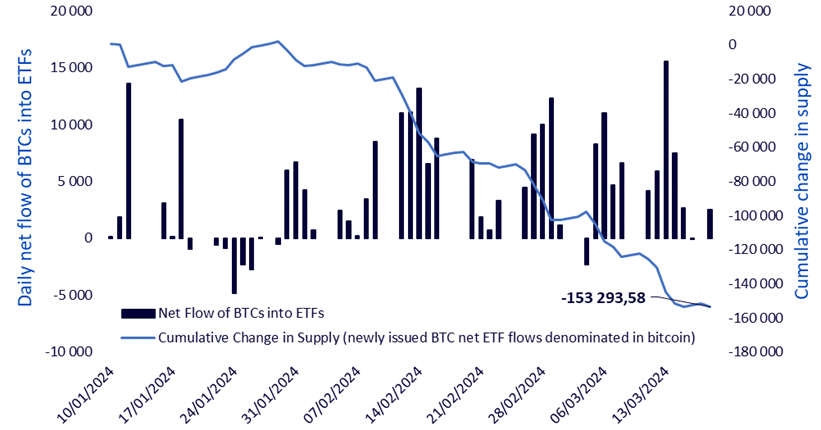
Source: Dune Analytics, Glassnode, as of March 25, 2024. Historical performance is no guarantee of future performance, and any investment may lose value.
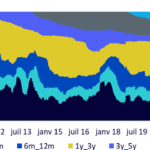
This may not always be the case and although the total market value of Bitcoin currently exceeds $1 trillion3, It is important to note that large volumes of Bitcoin are not actively traded. Analysis of transactions on the blockchain reveals that almost 30% of Bitcoins have been transferred to wallets in the last year, thus constituting the active supply. Therefore, this means that almost 70% of the supply remained inactive during this period. If this suggests that the argument for investing in Bitcoin as a long-term store of value or “digital gold” is starting to come to fruition, it could indicate that this dormant supply of Bitcoins is “not for sell”.
Illustration 3: Active supply of Bitcoins
Source: Glassnode, as of March 11, 2024. Historical performance is no guarantee of future performance, and any investment may lose value.
Will the next halving once again be synonymous with positive performance?
As investors continue their quest and refine their methods for developing price targets, we find it more informative to focus on supply and demand. If Bitcoin truly constitutes “digital gold,” it makes sense to take such an approach. At this point, it appears that demand for ETFs is strong and wallets are holding their Bitcoins for an extended period of time. However, we also know that halving is imminent, which will reduce new emissions. Each of these leads to a tightening of supply and a potential increase in demand thanks to the ease of access introduced with the launch of Bitcoin ETFs. If the wave of global adoption continues, all indicators suggest that the next halving cycle will generate strong performance.
1. Bitcoin is subject to a supply policy that strictly limits the number of Bitcoins created to 21 million units. This information is indicated in the Bitcoin code base, accessible here: https://github.com/bitcoin/bitcoin/blob/v25.0/src/consensus/amount.h (github.com, 2024).
2. Bitcoin is subject to a supply policy that strictly limits the number of Bitcoins created to 21 million units. This information is indicated in the Bitcoin code base, accessible here: https://github.com/bitcoin/bitcoin/blob/v25.0/src/consensus/amount.h (github.com, 2024).
3. CoinMarketCap, 2024.

